Problèmes connus
Cet article détaille les problèmes connus (et les solutions de contournement) relatifs à la partie logicielle du système de contrôle FRC®.
Questions ouvertes
AdvantageScope isn’t updated by WPILib Installer on macOS
Issue: When running the WPILib Installer, a pop-up saying "WPILibInstaller" was prevented from modifying apps on your Mac. and AdvantageScope remains version 3.0.1. This issue occurs when upgrading WPILib, when a beta version of WPIlib or WPILib 2024.1.1 was installed on macOS.
Workaround: Delete AdvantageScope from ~/wpilib/tools and re-run the WPILib Installer.
Driver Station randomly disabled
Issue: The Driver Station contains tighter safety mechanisms in 2024 to protect against control issues. Some teams have seen this cause the robot to disable.
Workaround: There are multiple potential causes for tripping the safety mechanisms.
Note
The new safety mechanisms will not disable the robot when connected to the FMS.
Driver Station 24.0.1 from Game Tools 2024 Patch 1 contains an update to the safety controls that may resolve the issue in certain circumstances. If the issue is still seen with this version installed, please continue with the troubleshooting steps below.
The Driver Station software has new tools for control packet delays that could cause this. The control system team requests that teams that experience this issue post screenshots of the Driver Station Timing window to https://github.com/wpilibsuite/allwpilib/issues/6174
Some teams have seen this happen only when the robot is operated wirelessly, but not when operated via USB or ethernet tether. Some potential mitigations:
Try relocating the robot radio to a better location (high in the robot and away from motors or large amounts of metal).
Measure your robot’s bandwidth and ensure you have margin to the 4 Mbps bandwidth limit
See if the Wi-Fi environment is congested using a tool like WiFi Analyzer. As the 5 ghz WiFi spectrum has more channels and is less crowded, switching the robot radio to operate at 5 ghz will likely improve WiFi communication.
Update the Wi-Fi drivers for the computer.
If you operate multiple robots in close proximity in access point mode, setting up a router and operating the radios in bridge mode will reduce the number of wireless access points and may improve communications
Some teams have seen this happen due to software that is running on the driver station (such as Autodesk updater or Discord). Some potential mitigations:
Reboot the driver station computer
Close software that is running in the background
Follow the Driver Station Best Practices
While rare, this can be caused by robot code that oversaturates the roboRIO processor or network connection. If all other troubleshooting steps fail, you can try running with one of the WPILib example programs to see if the problem still occurs.
If you identify software that interferes with driver station, please post it to https://github.com/wpilibsuite/allwpilib/issues/6174
Driver Station Reports Less Free RAM then is Available
Issue: The Driver Station diagnostic screen reports free RAM that is misleadingly low. This is due to Linux’s use of memory caches. Linux will cache data in memory, but then relinquish when the robot programs requests more memory. The Driver Station only reports memory that isn’t used by caches.
Workaround: The true memory available to the robot program is available in the file /proc/meminfo. Use ssh to connect to the robot, and run cat /proc/meminfo.
MemTotal: 250152 kB
MemFree: 46484 kB
MemAvailable: 126956 kB
The proper value to look is as MemAvailable, rather then MemFree (which is what the driver station is reporting).
Driver Station Reporting No Code
Issue: There is a rare occurrence in the roboRIO 2.0 that causes the roboRIO to not properly start the robot program. This causes the Driver Station to report a successful connection but no code, even though code is deployed on the roboRIO.
Workaround: We are currently investigating the root cause, but FIRST volunteers have been made aware and the recommendation is to reboot the roboRIO when this occurs.
Note
Pressing the physical User button on the roboRIO for 5 seconds can also cause the robot code to not start, but a reboot will not start the robot code. If the robot code does not start after rebooting, press the User button. Ensure that nothing on the robot is in contact with the User button.
Radio Second Port Sometimes Fails to Communicate
Issue: There is a rare occurrence in the OM5P Radios that causes the second Ethernet port (the one farthest from the power plug) to not communicate.
Workaround: Generally, power cycling the radio will restablish communication with the second port. Alternately, utilize a network switch such as the tp-link switch formerly available from FIRST Choice or the brainboxes SW-005 and plug all ethernet devices into the network switch and then plug the switch into the radio’s first Ethernet port. This also allows easier tethering while at competition.
Port I2C intégré provoquant des blocages du système
Issue: Use of the onboard I2C port on the roboRIO 1 or 2, in any language, can result in system lockups. The frequency of these lockups appears to be dependent on the specific hardware (i.e. different roboRIOs will behave differently) as well as how the bus is being used.
Workaround: The only surefire mitigation is to use the MXP I2C port or another device to read the I2C data. Accessing the device less frequently and/or using a different roboRIO may significantly reduce the likelihood/frequency of lockups, it will be up to each team to assess their tolerance of the risk of lockup. This lockup can not be definitively identified on the field and a field fault will not be called for a match where this behavior is believed to occur. This lockup is a CPU/kernel hang, the roboRIO will completely stop responding and will not be accessible via the DS, webpage or SSH. If you can access your roboRIO via any of these methods, you are experiencing a different issue.
Several alternatives exist for accessing the REV color sensor without using the roboRIO I2C port. A similar approach could be used for other I2C sensors.
Use a Raspberry Pi Pico. Supports up to 2 REV color sensors, sends data to the roboRIO via serial. The Pi Pico is low cost (less than $10) and readily available.
Use a Raspberry Pi. Supports 1-4 color sensors, sends data to the roboRIO via NetworkTables. Primarily useful for teams already using a Raspberry Pi as a coprocessor.
La mise à jour des propriétés du roboRIO 2.0 peut être lente ou bloquée
Problème: La mise à jour des propriétés d’un roboRIO 2.0 sans avoir à le reformatter à l’aide de l’outilitaire Imaging Tool (par exemple, la configuration du numéro d’équipe) peut être lente ou bloquée.
Solution: Après quelques minutes d’attente pendant l’exécution de l’outilitaire Imaging Tool, le roboRIO devrait pouvoir être redémarré et les nouvelles propriétés devraient être configurées.
Simulation crashes on Mac after updating WPILib
Issue: On macOS, after updating the project to use a newer version of WPILib, running simulation immediately crashes without the GUI appearing.
Workaround: In VS Code, run WPILib | Run a command in Gradle, clean. Alternatively, run ./gradlew clean in the terminal or delete the build directory.
Compilation invalide en raison de l’absence de GradleRIO
Problème: Très rare, le cache Gradle d’un utilisateur sera brisé et ils recevront des erreurs similaires à ce qui suit:
Could not apply requested plugin [id: ‘edu.wpi.first.GradleRIO’, version: ‘2020.3.2’] as it does not provide a plugin with id ‘edu.wpi.first.GradleRIO’
Solution de contournement:
Supprimez votre cache Gradle situé sous ~$USER_HOME/.gradle. Les machines Windows peuvent avoir besoin d’activer la possibilité de voir les fichiers cachés. Jusqu’à présent, ce problème n’est observé que sous Windows. S’il vous plaît signaler ce problème si vous l’observer sous un système d’exploitation alternatif.
Caractères chinois dans le journal du poste de conduite
Problème: Rarement, le journal du poste de conduite affichera des caractères chinois au lieu du texte anglais. Cela semble se produire uniquement lorsque Windows est défini sur une langue autre que l’anglais.
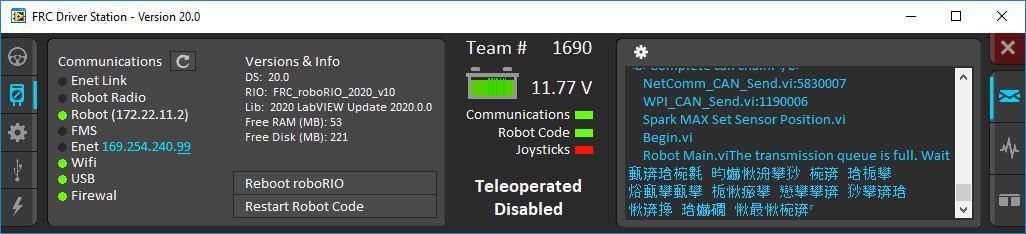
Solution de contournement: Il existe deux solutions de contournement connues:
Copiez et collez les caractères chinois dans le bloc-notes, et le texte anglais sera affiché.
Changez temporairement la langue de Windows en anglais.
C++ Intellisense - Les fichiers ouverts au lancement ne fonctionnent pas correctement
Problème: En C++, les fichiers ouverts au lancement de VS Code auront des problèmes avec Intellisense affichant les suggestions de toutes les options d’une unité de compilation et pas seulement celles appropriées ou ne trouvant pas de fichiers d’en-tête. Il s’agit d’un bogue dans VS Code.
Solution de contournement:
Fermez tous les fichiers dans VS Code, mais laissez VS Code ouvert
Supprimer le fichier c_cpp_properties.json dans le dossier .vscode, s’il existe
Run the « Refresh C++ Intellisense » command in VS Code.
En bas à droite, vous devriez voir quelque chose qui ressemble à une plate-forme (linuxathena ou windowsx86-64, etc.). S’il ne s’agit pas de linuxathena, cliquez dessus et définissez-le sur linuxathena (version)
Attendez ~ 1 min
Ouvrez le fichier cpp principal (pas un fichier d’en-tête avec extension .h). Intellisense devrait maintenant fonctionner
Problèmes avec les Dashboards WPILib et de simulation sur les éditions Windows N
Problème : Le code WPILib utilisant CSCore (dashboards et code robot simulé) aura des problèmes sur les versions Education N de Windows.
Le shuffleboard fonctionnera, mais ne chargera pas les caméras
Smartdashbard va planter au démarrage
La simulation de robot va planter au démarrage
Solution: Installez le Media Feature Pack
Fixed in WPILib 2024.2.1
Visual Studio Code Reports Unresolved Dependency
Issue: Java programs will report Unresolved dependency: org.junit.platform junit-platform-launcherJava(0) on build.gradle. Programs that use unit tests will fail to build. This causes build.gradle to be highlighted red in the Visual Studio Code explorer, and the plugins line in build.gradle to have a red squiggle.
Workaround: This can be safetly ignored if you aren’t running unit tests. To fix it, do the following:
On Windows execute the following in powershell:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/org/junit/jupiter/junit-jupiter/5.10.1/junit-jupiter-5.10.1.module -OutFile C:\Users\Public\wpilib\2024\maven\org\junit\jupiter\junit-jupiter\5.10.1\junit-jupiter-5.10.1.module
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/org/junit/junit-bom/5.10.1/junit-bom-5.10.1.module -OutFile C:\Users\Public\wpilib\2024\maven\org\junit\junit-bom\5.10.1\junit-bom-5.10.1.module
On Linux/macOS execute the following:
curl https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/org/junit/jupiter/junit-jupiter/5.10.1/junit-jupiter-5.10.1.module -o ~/wpilib/2024/maven/org/junit/jupiter/junit-jupiter/5.10.1/junit-jupiter-5.10.1.module
curl https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/org/junit/junit-bom/5.10.1/junit-bom-5.10.1.module -o ~/wpilib/2024/maven/org/junit/junit-bom/5.10.1/junit-bom-5.10.1.module
After running those, you’ll need to refresh Java intellisense in VS Code for it to pick up the new files. You can do so by running the Clean Java Language Server Workspace command in VS Code.