Conduire le robot avec le mode Tank Drive et Joysticks
Un cas d’utilisation courant est d’avoir un joystick qui devrait entraîner certains dispositifs actionneurs qui font partie d’un sous-système. Le problème est que le joystick est créé dans la classe OI et que les moteurs à contrôler sont dans le sous-système. L’idée est de créer une commande qui, lorsqu’elle est planifiée, lit les entrées du joystick et appelle une méthode créée sur le sous-système qui entraîne les moteurs.
Dans cet exemple, un sous-système de base d’entraînement est montré qui fonctionne en entraînement de réservoir à l’aide d’une paire de joysticks.
Créer un sous-système d’entraînement
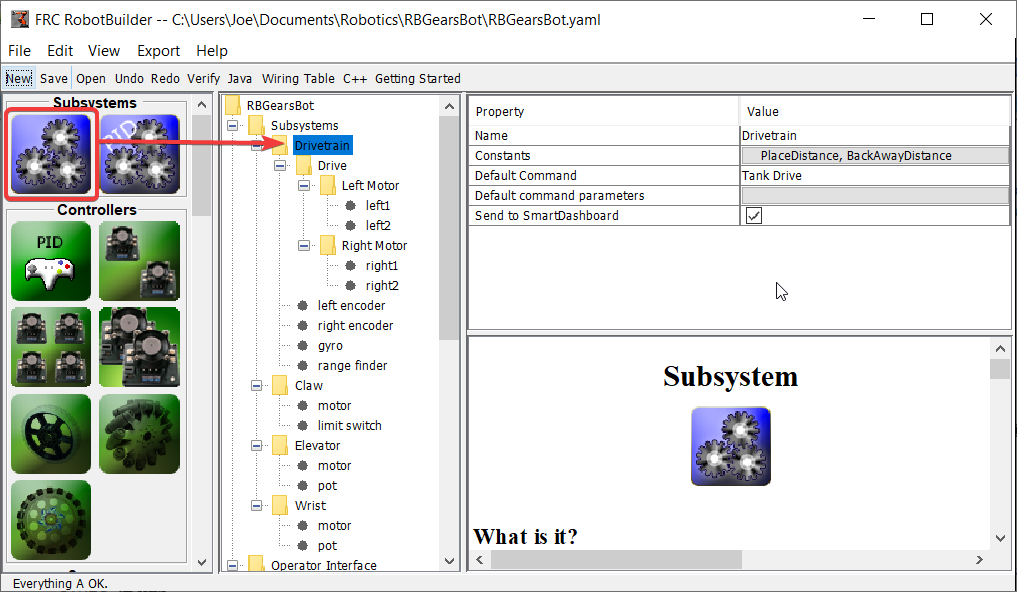
Créez un sous-système appelé Drive Train. Sa responsabilité sera de gérer la conduite de la base de robots.
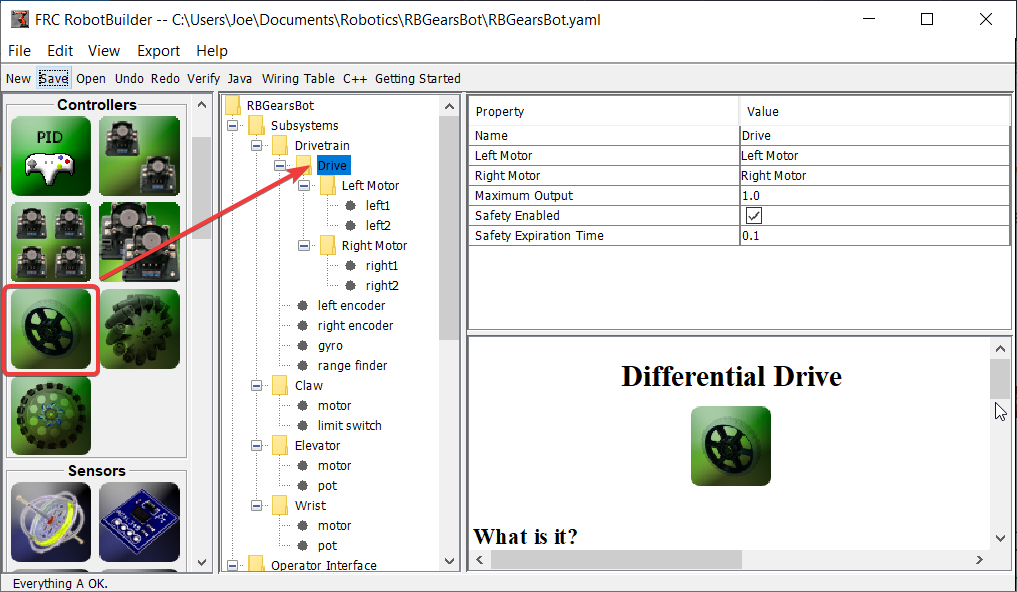
À l’intérieur du Drive Train créer un objet Differential Drive pour un entraînement à deux moteurs. Il y a un moteur gauche et un moteur droit dans le cadre de la classe Differential Drive.
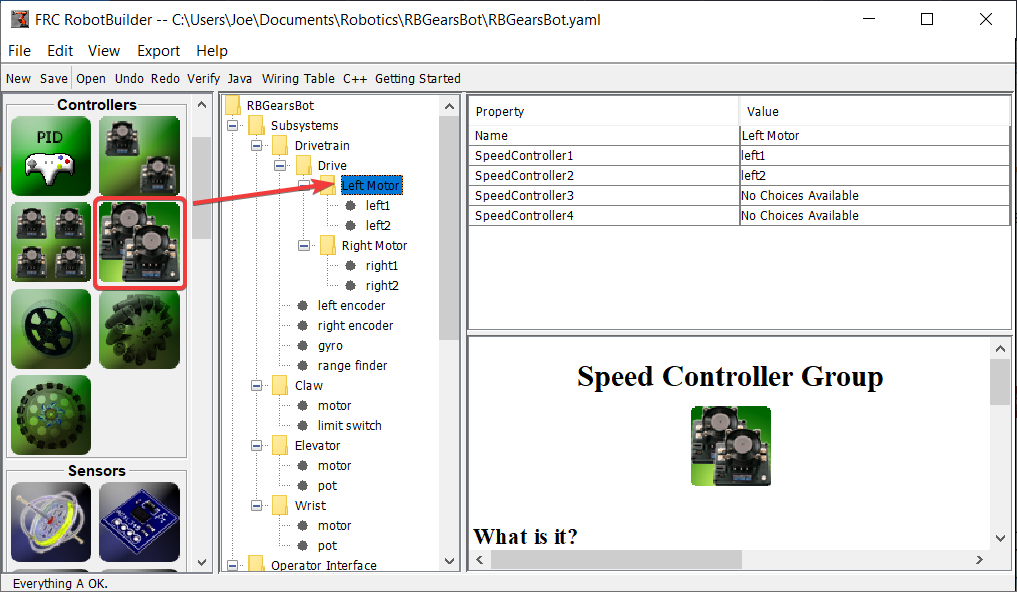
Puisque nous voulons utiliser plus de deux moteurs pour entraîner le robot, à l’intérieur de l’entraînement différentiel, créez deux groupes de contrôleurs de moteur. Ceux-ci regrouperont plusieurs contrôleurs de moteur afin qu’ils puissent être utilisés avec l’objet Differential Drive.
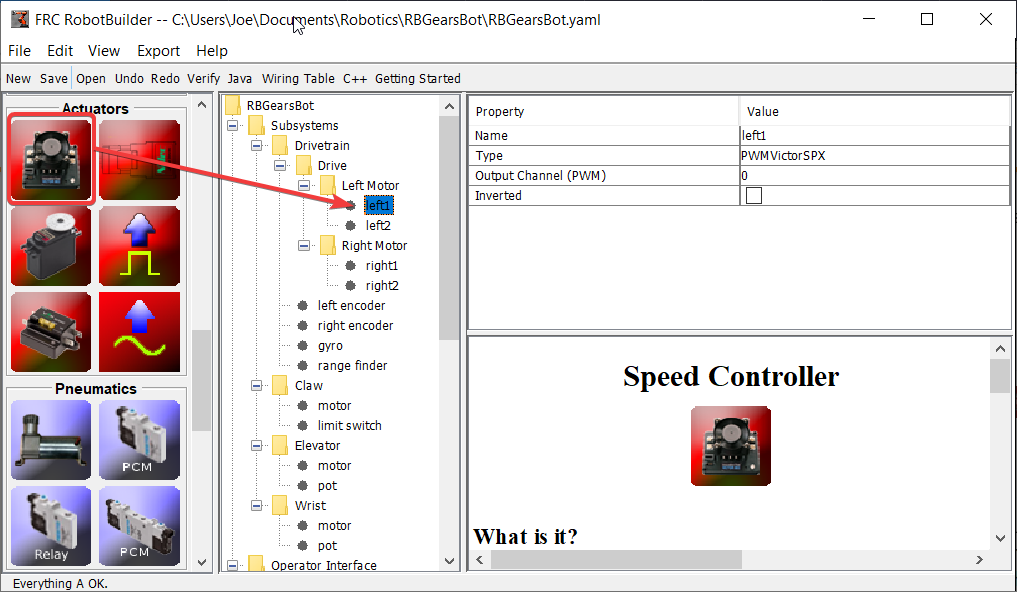
Enfin, créez deux contrôleurs de moteur dans chaque groupe de contrôleurs de moteur.
Ajouter les joysticks à l’interface opérateur
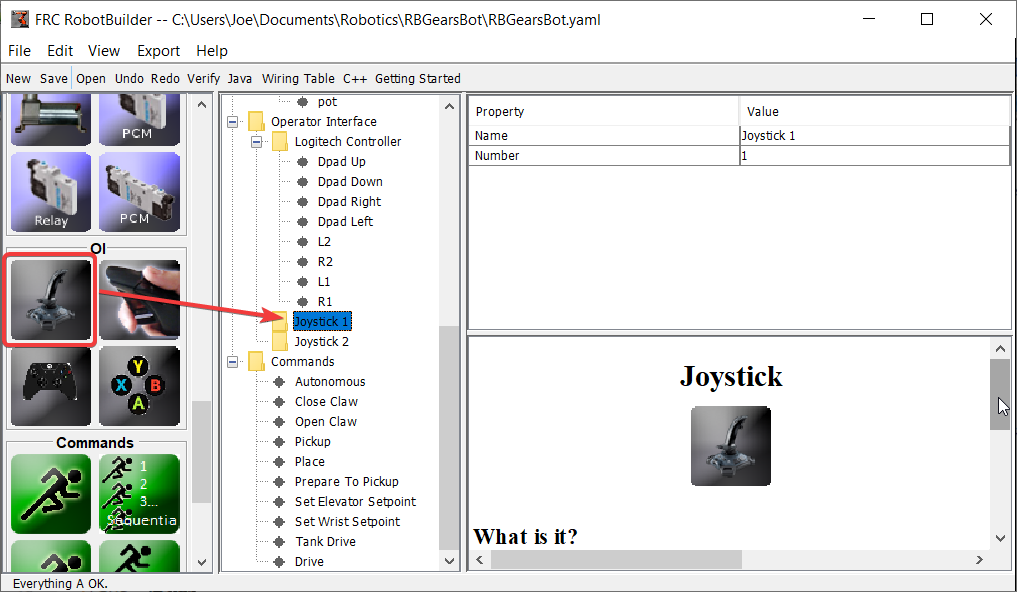
Ajoutez deux joysticks à l’interface opérateur, l’un est le joystick gauche et l’autre est le joystick droit. L’axe des y sur les deux joysticks est utilisé pour contrôler les moteurs gauche et droit du robot, respectivement.
Note
Assurez-vous d’exporter votre programme en C++ ou Java avant de passer à l’étape suivante.
Créer une méthode pour écrire aux moteurs dans le sous-système
11// ROBOTBUILDER TYPE: Subsystem.
12
13package frc.robot.subsystems;
14
15
16import frc.robot.commands.*;
17import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj.livewindow.LiveWindow;
18import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj2.command.SubsystemBase;
19
20// BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=IMPORTS
21import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj.AnalogGyro;
22import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj.AnalogInput;
23import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj.CounterBase.EncodingType;
24import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj.Encoder;
25import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj.drive.DifferentialDrive;
26import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj.motorcontrol.MotorController;
27import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj.motorcontrol.MotorControllerGroup;
28import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj.motorcontrol.PWMVictorSPX;
29
30 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=IMPORTS
31
32
33/**
34 *
35 */
36public class Drivetrain extends SubsystemBase {
37 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTANTS
38public static final double PlaceDistance = 0.1;
39public static final double BackAwayDistance = 0.6;
40
41 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTANTS
42
43 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=DECLARATIONS
44private PWMVictorSPX left1;
45private PWMVictorSPX left2;
46private MotorControllerGroup leftMotor;
47private PWMVictorSPX right1;
48private PWMVictorSPX right2;
49private MotorControllerGroup rightMotor;
50private DifferentialDrive drive;
51private Encoder leftencoder;
52private Encoder rightencoder;
53private AnalogGyro gyro;
54private AnalogInput rangefinder;
55
56 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=DECLARATIONS
57
58 /**
59 *
60 */
61 public Drivetrain() {
62 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTRUCTORS
63left1 = new PWMVictorSPX(0);
64 addChild("left1",left1);
65 left1.setInverted(false);
66
67left2 = new PWMVictorSPX(1);
68 addChild("left2",left2);
69 left2.setInverted(false);
70
71leftMotor = new MotorControllerGroup(left1, left2 );
72 addChild("Left Motor",leftMotor);
73
74
75right1 = new PWMVictorSPX(5);
76 addChild("right1",right1);
77 right1.setInverted(false);
78
79right2 = new PWMVictorSPX(6);
80 addChild("right2",right2);
81 right2.setInverted(false);
82
83rightMotor = new MotorControllerGroup(right1, right2 );
84 addChild("Right Motor",rightMotor);
85
86
87drive = new DifferentialDrive(leftMotor, rightMotor);
88 addChild("Drive",drive);
89 drive.setSafetyEnabled(true);
90drive.setExpiration(0.1);
91drive.setMaxOutput(1.0);
92
93
94leftencoder = new Encoder(0, 1, false, EncodingType.k4X);
95 addChild("left encoder",leftencoder);
96 leftencoder.setDistancePerPulse(1.0);
97
98rightencoder = new Encoder(2, 3, false, EncodingType.k4X);
99 addChild("right encoder",rightencoder);
100 rightencoder.setDistancePerPulse(1.0);
101
102gyro = new AnalogGyro(0);
103 addChild("gyro",gyro);
104 gyro.setSensitivity(0.007);
105
106rangefinder = new AnalogInput(1);
107 addChild("range finder", rangefinder);
108
109
110
111 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTRUCTORS
112 }
113
114 @Override
115 public void periodic() {
116 // This method will be called once per scheduler run
117
118 }
119
120 @Override
121 public void simulationPeriodic() {
122 // This method will be called once per scheduler run when in simulation
123
124 }
125
126 // Put methods for controlling this subsystem
127 // here. Call these from Commands.
128
129 public void drive(double left, double right) {
130 drive.tankDrive(left, right);
131 }
132}
11// ROBOTBUILDER TYPE: Subsystem.
12#pragma once
13
14// BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=INCLUDES
15#include <frc2/command/SubsystemBase.h>
16#include <frc/AnalogGyro.h>
17#include <frc/AnalogInput.h>
18#include <frc/Encoder.h>
19#include <frc/drive/DifferentialDrive.h>
20#include <frc/motorcontrol/MotorControllerGroup.h>
21#include <frc/motorcontrol/PWMVictorSPX.h>
22
23// END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=INCLUDES
24
25/**
26 *
27 *
28 * @author ExampleAuthor
29 */
30class Drivetrain: public frc2::SubsystemBase {
31private:
32 // It's desirable that everything possible is private except
33 // for methods that implement subsystem capabilities
34 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=DECLARATIONS
35frc::AnalogInput m_rangefinder{1};
36frc::AnalogGyro m_gyro{0};
37frc::Encoder m_rightencoder{2, 3, false, frc::Encoder::k4X};
38frc::Encoder m_leftencoder{0, 1, false, frc::Encoder::k4X};
39frc::DifferentialDrive m_drive{m_leftMotor, m_rightMotor};
40frc::MotorControllerGroup m_rightMotor{m_right1, m_right2 };
41frc::PWMVictorSPX m_right2{6};
42frc::PWMVictorSPX m_right1{5};
43frc::MotorControllerGroup m_leftMotor{m_left1, m_left2 };
44frc::PWMVictorSPX m_left2{1};
45frc::PWMVictorSPX m_left1{0};
46
47 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=DECLARATIONS
48public:
49Drivetrain();
50
51 void Periodic() override;
52 void SimulationPeriodic() override;
53 void Drive(double left, double right);
54 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CMDPIDGETTERS
55
56 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CMDPIDGETTERS
57 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTANTS
58static constexpr const double PlaceDistance = 0.1;
59static constexpr const double BackAwayDistance = 0.6;
60
61 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTANTS
62
63
64};
11// ROBOTBUILDER TYPE: Subsystem.
12
13// BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=INCLUDES
14#include "subsystems/Drivetrain.h"
15#include <frc/smartdashboard/SmartDashboard.h>
16
17// END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=INCLUDES
18
19Drivetrain::Drivetrain(){
20 SetName("Drivetrain");
21 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=DECLARATIONS
22 SetSubsystem("Drivetrain");
23
24 AddChild("range finder", &m_rangefinder);
25
26
27 AddChild("gyro", &m_gyro);
28 m_gyro.SetSensitivity(0.007);
29
30 AddChild("right encoder", &m_rightencoder);
31 m_rightencoder.SetDistancePerPulse(1.0);
32
33 AddChild("left encoder", &m_leftencoder);
34 m_leftencoder.SetDistancePerPulse(1.0);
35
36 AddChild("Drive", &m_drive);
37 m_drive.SetSafetyEnabled(true);
38m_drive.SetExpiration(0.1_s);
39m_drive.SetMaxOutput(1.0);
40
41
42 AddChild("Right Motor", &m_rightMotor);
43
44
45 AddChild("right2", &m_right2);
46 m_right2.SetInverted(false);
47
48 AddChild("right1", &m_right1);
49 m_right1.SetInverted(false);
50
51 AddChild("Left Motor", &m_leftMotor);
52
53
54 AddChild("left2", &m_left2);
55 m_left2.SetInverted(false);
56
57 AddChild("left1", &m_left1);
58 m_left1.SetInverted(false);
59
60 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=DECLARATIONS
61}
62
63void Drivetrain::Periodic() {
64 // Put code here to be run every loop
65
66}
67
68void Drivetrain::SimulationPeriodic() {
69 // This method will be called once per scheduler run when in simulation
70
71}
72
73// BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CMDPIDGETTERS
74
75// END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CMDPIDGETTERS
76
77
78// Put methods for controlling this subsystem
79// here. Call these from Commands.
80
81 void Drivetrain::Drive(double left, double right) {
82 m_drive.TankDrive(left, right);
83 }
Create a method that takes the joystick inputs, in this case the left and right driver joystick. The values are passed to the DifferentialDrive object that in turn does tank steering using the joystick values. Also create a method called stop() that stops the robot from driving, this might come in handy later.
Note
Certaines sorties du RobotBuilder ont été supprimées dans cet exemple pour plus de clarté
Lire les valeurs des joysticks et appeler les méthodes du sous-système
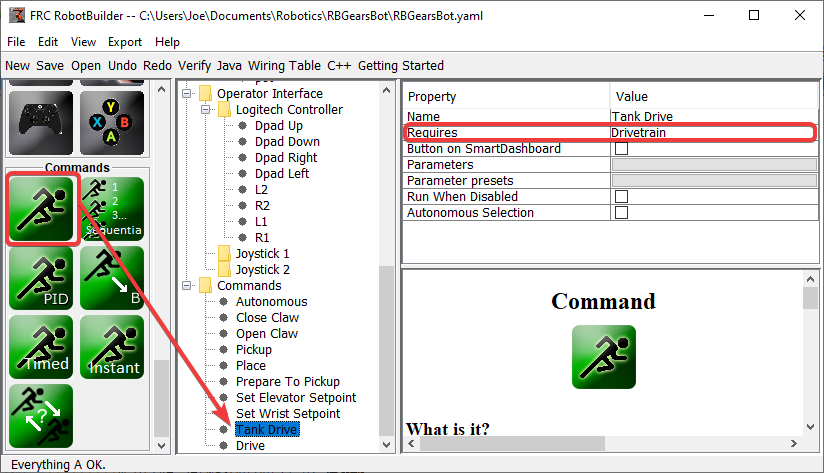
Créez une commande, dans ce cas appelée Tank Drive. Son but sera de lire une valeur de joystick et de la renvoyer au sous-système « Drive Base ». Notez que cette commande nécessite le sous-système « Drive Train ». Ce qui fera en sorte que cette commande cessera de fonctionner chaque fois que quelque chose d’autre tentera d’utiliser le « Drive Train »
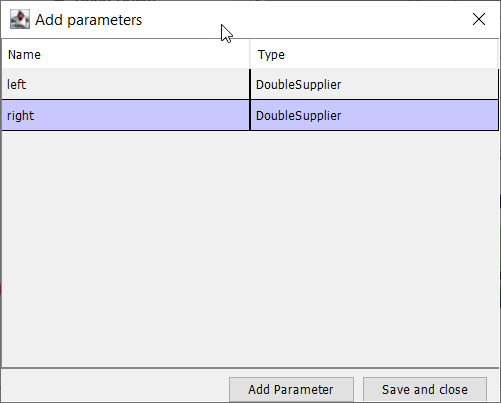
Create two parameters (DoubleSupplier for Java or std::function<double()> for C++) for the left and right speeds.
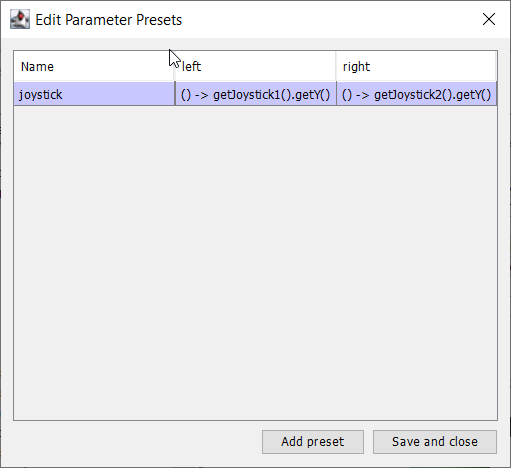
Create a parameter preset to retrieve joystick values. Java: For the left parameter enter () -> getJoystick1().getY() and for right enter () -> getJoystick2().getY(). C++: For the left parameter enter [this] {return getJoystick1()->GetY();} and for the right enter [this] {return getJoystick2()->GetY();}
Note
Assurez-vous d’exporter votre programme en C++ ou Java avant de passer à l’étape suivante.
Ajoutez le code pour conduite le robot
11// ROBOTBUILDER TYPE: Command.
12
13package frc.robot.commands;
14import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj.Joystick;
15import edu.wpi.first.wpilibj2.command.CommandBase;
16import frc.robot.RobotContainer;
17// BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=IMPORTS
18import frc.robot.subsystems.Drivetrain;
19
20 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=IMPORTS
21
22/**
23 *
24 */
25public class TankDrive extends CommandBase {
26
27 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=VARIABLE_DECLARATIONS
28 private final Drivetrain m_drivetrain;
29
30 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=VARIABLE_DECLARATIONS
31
32 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTRUCTORS
33
34
35 public TankDrive(Drivetrain subsystem) {
36
37
38 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTRUCTORS
39 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=VARIABLE_SETTING
40
41 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=VARIABLE_SETTING
42 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=REQUIRES
43
44 m_drivetrain = subsystem;
45 addRequirements(m_drivetrain);
46
47 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=REQUIRES
48 }
49
50 // Called when the command is initially scheduled.
51 @Override
52 public void initialize() {
53 }
54
55 // Called every time the scheduler runs while the command is scheduled.
56 @Override
57 public void execute() {
58 m_drivetrain.drive(m_left.getAsDouble(), m_right.getAsDouble());
59 }
60
61 // Called once the command ends or is interrupted.
62 @Override
63 public void end(boolean interrupted) {
64 m_drivetrain.drive(0.0, 0.0);
65 }
66
67 // Returns true when the command should end.
68 @Override
69 public boolean isFinished() {
70 return false;
71 }
72
73 @Override
74 public boolean runsWhenDisabled() {
75 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=DISABLED
76 return false;
77
78 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=DISABLED
79 }
80}
11// ROBOTBUILDER TYPE: Command.
12
13#pragma once
14
15 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=INCLUDES
16
17#include <frc2/command/CommandHelper.h>
18#include <frc2/command/CommandBase.h>
19
20#include "subsystems/Drivetrain.h"
21
22 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=INCLUDES
23#include "RobotContainer.h"
24#include <frc/Joystick.h>
25
26/**
27 *
28 *
29 * @author ExampleAuthor
30 */
31class TankDrive: public frc2::CommandHelper<frc2::CommandBase, TankDrive> {
32public:
33 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTRUCTOR
34 explicit TankDrive(Drivetrain* m_drivetrain);
35
36 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTRUCTOR
37
38void Initialize() override;
39void Execute() override;
40bool IsFinished() override;
41void End(bool interrupted) override;
42bool RunsWhenDisabled() const override;
43
44
45private:
46 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=VARIABLES
47
48
49Drivetrain* m_drivetrain;
50frc::Joystick* m_leftJoystick;
51frc::Joystick* m_rightJoystick;
52
53 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=VARIABLES
54};
11// ROBOTBUILDER TYPE: Command.
12
13// BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTRUCTOR
14
15#include "commands/TankDrive.h"
16
17TankDrive::TankDrive(Drivetrain* m_drivetrain)
18:m_drivetrain(m_drivetrain){
19
20 // Use AddRequirements() here to declare subsystem dependencies
21 // eg. AddRequirements(m_Subsystem);
22 SetName("TankDrive");
23 AddRequirements({m_drivetrain});
24
25// END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=CONSTRUCTOR
26}
27
28// Called just before this Command runs the first time
29void TankDrive::Initialize() {
30
31}
32
33// Called repeatedly when this Command is scheduled to run
34void TankDrive::Execute() {
35 m_drivetrain->Drive(m_left(),m_right());
36}
37
38// Make this return true when this Command no longer needs to run execute()
39bool TankDrive::IsFinished() {
40 return false;
41}
42
43// Called once after isFinished returns true
44void TankDrive::End(bool interrupted) {
45 m_drivetrain->Drive(0,0);
46}
47
48bool TankDrive::RunsWhenDisabled() const {
49 // BEGIN AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=DISABLED
50 return false;
51
52 // END AUTOGENERATED CODE, SOURCE=ROBOTBUILDER ID=DISABLED
53}
Add code to the execute method to do the actual driving. All that is needed is pass the for the left and right parameters to the Drive Train subsystem. The subsystem just uses them for the tank steering method on its DifferentialDrive object. And we get tank steering.
Nous avons également rempli la méthodes end() afin que lorsque cette commande est interrompue ou arrêtée, les moteurs soient arrêtés par mesure de sécurité.
Créer une commande par défaut
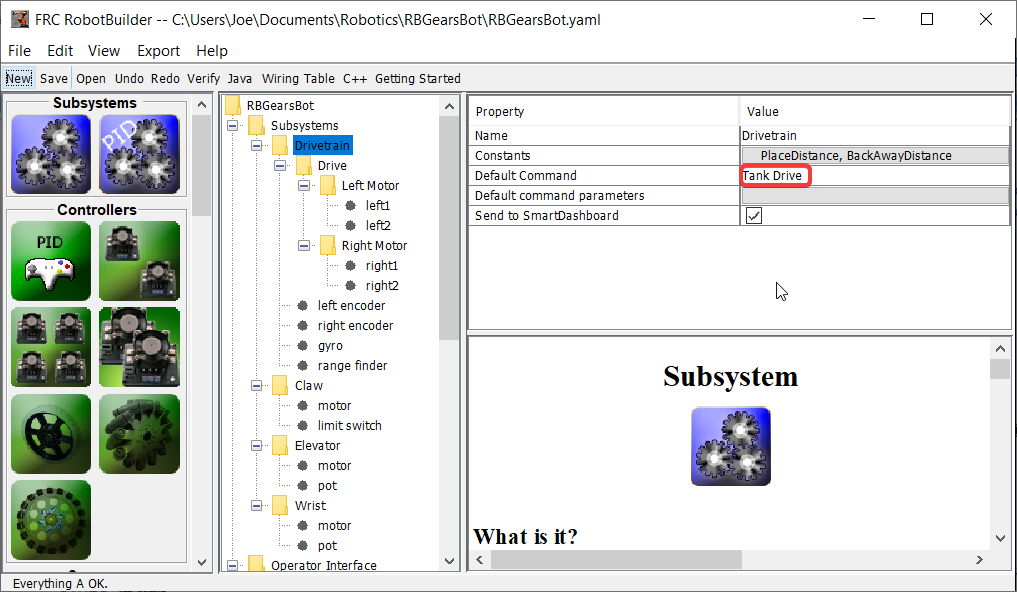
La dernière étape consiste à faire de la commande Tank Drive la « commande par défaut » du sous-système « Drive Train ». Cela signifie que les joysticks seront en contrôle tout le temps de la conduite, sauf lorsqu’une autre commande va utiliser « Drive Train ». C’est probablement le comportement souhaitable. Lorsque le code du mode autonome est en cours d’exécution, il nécessitera également « Drive Train » et interrompra la commande Tank Drive. Une fois le code autonome terminé, la commande Tank Drive redémarrera automatiquement (car il s’agit de la commande par défaut) et les opérateurs reprendront le contrôle. Si vous écrivez un code qui effectue une conduite automatisée (en se servant de capteurs, par exemple), ces commandes nécessitent également le DriveTrain et elles aussi vont interrompre la commande Tank Drive pour et prendre le contrôle du déplacement.
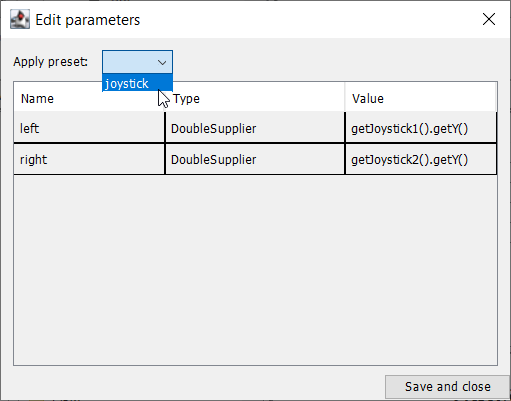
The final step is to choose the joystick parameter preset previously set up.
Note
Assurez-vous d’exporter votre programme en C++ ou Java avant de continuer.